Globalization and complexity in supply chains
In a not too distant past, certain business practices that led to logistics to reach the level it is today appeared. Some of them remain, but others have emerged that are creating new trends in the supply chain, taking it to different directions of current. This article aims to show what these business trends and what consequences will bring – if confirmed – to supply chains and also the daily lives of professionals working in the sector.
The article will address initially the historical evolution of logistics, showing how we arrived at the current point and why some trends remain in vogue. Then review the new challenges and opportunities, highlighting aspects that may impact the supply chain.
Predictions are not always confirmed, but there is something we can say with relative confidence: supply chains become more complex as a consequence of globalization.
And how to deal with the complexity passes obligatorily by industry professionals. The human resource management is now a major concern for companies. Not coincidentally, the recruitment sector is rising in importance in the hierarchy of companies in the United States because it needs to attract, train and retain the right people to manage their supply chain.
Evolution of Logistics
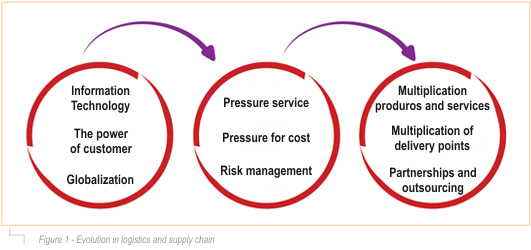
How, in recent decades, the supply chain began to evolve and what were the factors that influenced this evolution? Among the main motivators triggers must list the information technology, globalization and the power of customers, and verify how they generated the pressures that all professional feel to your everyday life, such as cost management, service delivery and risk management. These pressures, in turn, forced companies to take measures to ensure its viability in the market and also added complexity in their supply chains: the multiplication of products and services, expansion of delivery points and outsourcing. The latter increased the number of partners of firms in their supply chains.
Information technology. The exponentially decreasing cost of manipulating the information remains a major transformation of our times and affects not only the supply chain. I believe that when future historians portray the current time, which further highlight will be the IT, as this has evolved dramatically impacted and how humanity.
For example, when I came to the U.S. in the 1970s, the letters sent by mail to my family in Brazil took a week to arrive. The response took a further week. Today, we talk on Skype instantly. This change occurred within about 40 years, which is nothing in terms of human development. Just four decades, speaking by Skype seem science fiction.
This technological evolution has brought with it the ability to handle a huge amount of data and information. The bar code, for example, allowed firms access to a large number of data to make decisions, maintain customer information, analyze costs and try to reduce them.
This has been increasing exponentially over the years and keeps growing. Currently, many mobile phones have more processing power than the larger computers had a few decades ago. In parallel, there was an equally exponential reduction in the cost of computers and software, which can now be obtained for a fraction of that cost in the recent past.
Globalization
Alongside the development of IT, and also because of it, there was an acceleration of the globalization phenomenon. Countries are less distant, economies are more integrated and interdependent and increasingly, companies have suppliers and customers in various countries. The technologies that connect the corporate sector and the countries themselves traveling with more speed than in the past, helping to reduce the boundaries of the planet.
Globalization generates a fierce competition between companies, it opens new markets to regional or global competitors. Companies that previously did not have much competition, maybe one or two local competitors, now face companies worldwide. As a result, globalization creates pressure for quality and strong cost.
The power of the client
This is a phenomenon which has been increasing over the past decades and directly influences the supply chain. Historically, the distribution channels were controlled by manufacturers institutions. They were dictating conditions for retail, which was then composed, mainly by small companies and smaller manufacturers.
During the 1950s and part of 1960, the United States, manufacturers had such force that there were laws forcing retailers to sell products at a price determined by them. These laws were based on the manufacturers had invested in innovation and marketing and therefore had the right to avoid argument that retailers depreciassem product with a low price. This idea today would certainly not have much acceptance.
What happened over the years? Due to the growth of the economy, with the emergence of large retail chains in the U.S. and other countries, most supply chains are controlled by large retailers, imposing different conditions from those that manufacturers imposed in the past.
To control the supply chain, manufacturers typically invest intensively in their brands. Apple is one example. Consequently, control the retail because they know that the end consumer wants to buy your brand. Thus, impose commercial conditions such as price and logistics services. The retailer, which needs the manufacturer’s brand to attract customers at a disadvantage in the supply chain.
But this is the exception in today’s world. In most cases, those who have greater market presence and maintains greater consumer loyalty is the retailer. Consumers are loyal to Home Depot, to Toys R Us and so on. In this case it is the manufacturer that the retailer needs to access the market. And what the retailer requires the manufacturer is not necessarily a strong brand, but price and logistics services. To better manage its supply chain, the retailer requires deliveries on time, without damage or errors in the specified packaging and delivery with advanced notification. This transfer of power has transformed the supply chain, making it extremely important logistics service in the customer-supplier relationship.
Another example of strong customer besides the great retail, is the automotive industry, which requires its suppliers to deliver products just-in-time model to reduce inventory, and to locate themselves close to the plant to reduce transportation costs.
This was therefore the evolution of the business that consequently brought the great growth of the logistics model. There is information technology in supply chains that enables companies to operate globally both in sales and in supply and at the same time, strong customers who require these same companies offering products and logistics services at competitive costs. The technology enables the competition requires.
Risk
In addition, we have the logistics to have the dual role of providing a good level of service to customers and at the same time contribute to the reduction of product cost. As a result, the current supply chains operate with less inventory and shorter lead times. This success brought the trailer, the need for risk management. As the client begins to trust in supplier delivery, reduce your safety stock (to reduce their own cost) and start taking risks. If a delivery delay, there is an increased risk of shortage than there were in the past, when stocks were the biggest customer. Likewise, the more globalized the company, the higher the risk exposure because the supply chain gets longer and more exposed to unforeseen events.
Moreover, the company not to reduce cost not to take risks, live with the certainty of higher cost. Therefore, enterprises have to manage risk in two basic categories. One is operational risk, which reflects daily changes in customer demand and changes in the delivery of suppliers. The other category is the catastrophic risk, which reflects low probability events to occur, but with severe consequences when they occur, such as earthquakes, hurricanes and tsunamis, for example. Gambling is no excuse, the risk has to be managed.
Multiplicity
The three trends discussed in this article also affected other characteristics of the supply chain, because it led to increased complexity of logistics work. These characteristics are the multiplication of products and services, delivery points and partnerships.
Multitude of products. As already mentioned, globalization increases the level of competition. When this happens, the marketing becomes important because one of the main ways to compete is through the development of new products. The largest number of products on the market adds complexity to the supply chain.
In the past, for example, the variety of shoes available to consumers was very low. Only two colors: white or black. Today, there is a wide variety of designs and colors available. The market for shoes has become a fashion market where products change constantly.
And what is the implication for the supply chain? Apart from the manufacturing process, it requires a more complex supply chain. The error in forecasting sales tend to be higher. The inventory level in store is also higher because the retailer of shoes have to keep stock of all new products in all sizes, colors and in all stores. As this level of investment in stock is usually not possible, the stores have to maintain lower inventories and be replenished very quickly and often. The Quick Response – or quick response to the consumer – emerged largely due to the need. The logistics service fast delivery enables the marketing strategy.
Multiplicity of points of delivery. Currently, the number of delivery points is also much larger than in the past. The notion of “scrambled merchandising” or “scrambled marketing” expresses the fact that products are today available to consumers in non-traditional forms of retailing. For example, you can buy medicines and food at the grocery store in the pharmacy; is also possible to buy oil for the car at the supermarket, food at the gas station and so on. All this leads to greater complexity, which should facilitate the logistics.
Multiplicity of business partners. Finally, due to the increased competition, there was also the growth of partnerships and outsourcing. The more competitive a market, the greater the need to be competent in all aspects of logistics. This is because the “weak point”, is shipping cost, quality of service, etc.., Prevents the company from being competitive with the market. In a situation of low level of competition, the company can afford to have weaknesses in their logistics. For example, it may have an area of inefficient transport and other areas – such as inventory and services – with better performance. Thus, on average, the company is within the level of competition, whereas its competitors are not much better.
As competition increases, the company can not only be competent in some ways because your competitor is now better at all. The company is then pressed to raise their competitiveness quickly. And one of the most efficient ways to do this is by outsourcing the less efficient areas. The company passes the responsibility for these areas for someone who is an expert, who has more experience, applied technology, economies of scale, etc.. This reduces your costs and can offer more competitive prices and services.
Therefore, globalization has generated demand for partnerships and outsourcing. In competitive markets, the rule is developing its supply chain not only their own resources, but also with external resources.
This is the trend we have seen over the years and this is how we got to the current state of supply chain management. In the second part of this article, we will see the impact of these trends on the current supply chains and also the implications for their management.
Source: http://www.tecnologistica.com.br/