Meios de comunicação e o avanço da Internet

The search for information has always been a characteristic of human beings. The older system of mass communication is the radio: it can, through frequency or amplitude modulated (FM or AM), transmit information to thousands of people. His most famous successor is television, broadcasting sound and image by VHF (Very High Frequency – Frequency Very High) and UHF (Ultra High Frequency – Ultra High Frequency).
But as people are always looking for more ways to socialize, exchange of information and knowledge, only those means were not enough. Thus, the greatest advancement of humanity today, related to communication was the Internet. She started shy in the 1960s in American universities and is currently the fastest and practical way of communication, but is she is quick even?
In Brazil, the onset of the Internet has given to the use of modems connected to telephone lines, to be a basic and existing infrastructure. This system was known as narrowband or dial up (dial-up), because his speed was greatly reduced and reached up to 56 Kbps only. Another inconvenience was when the internet was connected: used the telephone line, making it impossible to use it. To try to tackle the problem of speed and line busy, operators began using ADSL (assymetrical Digital Subscriber Line – Line Asymmetric Digital Subscriber to), allowing the simultaneous use of the Internet and telephone. When using the telephone infrastructure (cables, poles, terminal boxes and call centers), distance limitations happen and the internet speed can be varied; thus, the greater the distance between the subscriber’s home and the telephone exchange, the lower the speed offered.
With current advances in technology, there are fiber optic networks, which are under implementation in restricted regions of Brazil. This technology solves the problem of distance and speed, because it uses a transparent glass filament with a high degree of purity. Around the filament, no substances having a lower refractive index, which makes the rays are internally reflected and minimize transmission losses. This technology allows the loading of thousands of digital information without significant losses, presenting ability to transmit very high data rates in the order of Gbps (billion bits per second).
These characteristics of the optical fiber, added to the fact that their communication systems using lasers or light-emitting devices (LEDs), make the transmitted data are immune to electromagnetic interference and noise, not to radiate light out of the cable. As for this technology are needed equipment for media conversion, telephone companies are beginning to offer this option to customers and implementing the required system.
A testament to the quality that optical fiber offers communication is here: Google announced in late 2014 that it will build a fiber optic submarine cable between the United States and Brazil. According to the company, the network will have more than 10 thousand kilometers.
But why Google will do it? To improve the telecommunications infrastructure of Brazil, currently lacking. And of course, for strategic reasons, since Google posted there nearly 300 million online users in Latin America.
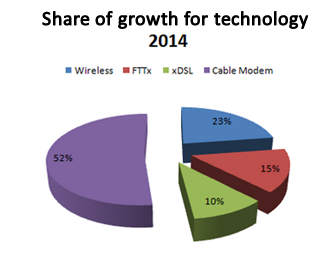
The Anatel’s report shows that the optical technology is already growing in Brazil, because in 2014 hits per FFTx, technology allows lead to fiber to the home subscriber, increased by 34.3%. But the cable modem also has the greatest growth. Comparing 2013 and 2014, increased 12.7%, with 52% of total accesses in Brazil, as shown in the image below.
Brazil has great potential in relation to the growth of broadband, but the quality leaves to be desired. According to a report by Akamai Internet company, the country is in 89th position in the global ranking of fixed average internet speed. South Korea has the best average with 23.6 Mbps; Second are Ireland (17.4 Mbps), followed by Hong Kong (16.7 Mbps), Sweden (15.8 Mbps) and the Netherlands (15.3 Mbps).
Another issue related to communication, and that is not news to anyone, is that smartphones and tablets are increasingly used by people to access the Internet. This information is confirmed by recent research by the IBGE (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics), concluding that 57.3% of households accessed the Internet via mobile phones and tablets in 2013.
Thus, it is more than time for operators to offer an adequate internet and meets the needs of its consumers. Therefore, improve the speed of 4G networks and its scope to thus provide a true mobile broadband, should be a primary concern for operators.
Full article: http://corporate.canaltech.com.br